Types of Wires and Cables and Their Features
what will you read...
What are Wires and CablesStructure of Wires and CablesConductor Types: Copper and AluminumCopper Conductor FeaturesAluminum Conductor FeaturesInsulation of Wires and Cables: PVC, XLPE, and Other MaterialsPVC InsulationXLPE InsulationSheath and Shielding in Wires and CablesShieldingArmoringTypes of Wires and Cables1Power Transmission Cables (High and Low Voltage)2Telecommunication Cables3Signal Transmission Cables4Control Cables5Instrumentation Cables6Network Cables7Other CablesApplications of Different Wires and CablesConclusionWires and cables are essential components in various industries, including construction, electricity transmission, and telecommunications. Given the high importance of these products in daily life, understanding their structure, conductor types, insulation, and coatings, as well as their applications, can lead to better selection for different uses. In this article, we will review the types of wires and cables from various aspects
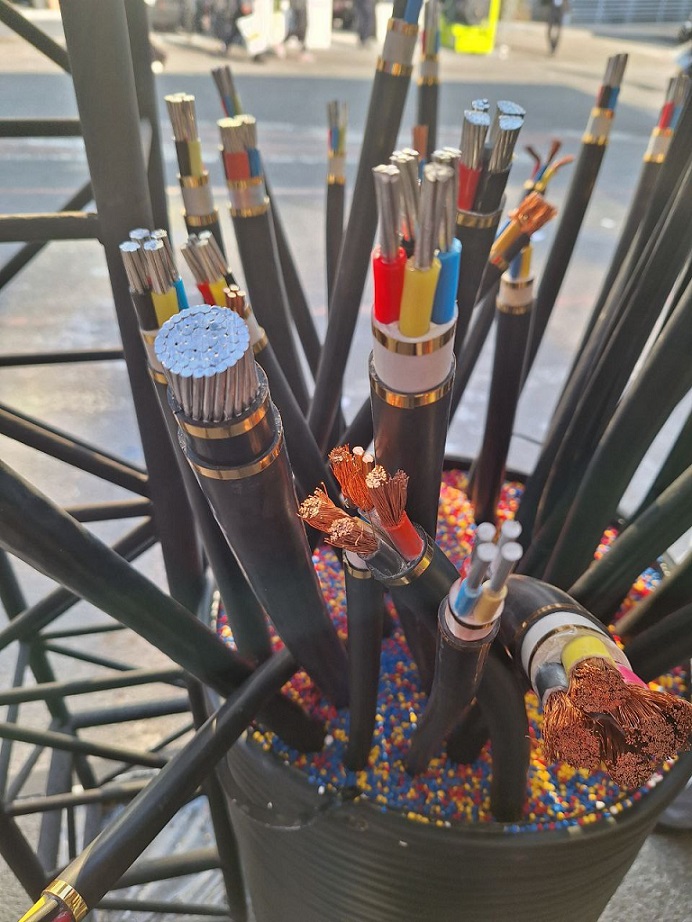

What are Wires and Cables
A wire generally refers to a single strand or multiple strands of metal that are responsible for carrying electrical current or signals. Wires can be single-stranded or multi-stranded, and depending on their application, they may have different insulating coatings
A cable, in fact, is a collection of wires that are grouped together and typically insulated and coated to protect them from environmental and mechanical factors. Cables may contain several conductive wires that are separately insulated but housed within one outer protective cover. Cables are typically used for transmitting electrical power, data, or signals in complex systems. Depending on their application, cables may also include features such as shielding and armoring

Structure of Wires and Cables
The structure of wires and cables typically consists of a conductor, insulation, outer sheath, and sometimes shielding and armoring. The conductor, being the core component, is responsible for transmitting electrical current or signals. The insulation’s role is to separate the conductors from each other and prevent unauthorized connections or energy losses. The outer sheath is usually made from materials resistant to environmental conditions to protect the cable from external damage.
Conductor Types: Copper and Aluminum
The conductors in wires and cables can be made of copper or aluminum. Copper, due to its high electrical conductivity and low resistance, is generally the first choice for power and signal cables. On the other hand, aluminum, being lighter and more cost-effective, is often used as a more economical option for certain applications. Both materials have unique features, and their selection depends on the specific needs of the project and environmental conditions

Copper Conductor Features
Excellent electrical conductivity
Low resistance to current flow
Long lifespan
Aluminum Conductor Features
Lighter than copper
Lower cost
Greater flexibility
Insulation of Wires and Cables: PVC, XLPE, and Other Materials
Insulations are designed to protect conductors from external environments, moisture, and mechanical damage. Common materials used in insulation include PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene). Each of these materials has unique characteristics that allow them to be used in different environments

PVC Insulation
High flexibility
Moderate resistance to environmental conditions
Cost-effective
XLPE Insulation
Excellent resistance to high temperatures
Resistance to chemicals and environmental factors
Suitable for industrial and construction applications
Sheath and Shielding in Wires and Cables
Sheath and shields are typically used to increase resistance against environmental factors, signal interference, or mechanical damage. Sheaths are generally made from PVC or similar materials and are resistant to water, chemicals, and UV rays

Shielding
Shields are typically made from metal strands, such as copper or aluminum, and are used to protect cables from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electrical noise. This feature is particularly important in cables used in data and telecommunications networks
Armoring
Armors are usually made from durable metals such as steel and are designed to protect cables from pressure and physical damage. These cables are used in environments where there is a high risk of damage, such as construction sites or areas with challenging conditions
Types of Wires and Cables
1Power Transmission Cables (High and Low Voltage)
These cables are used to transmit electrical energy in various industries and electrical distribution networks. Power cables can include copper or aluminum conductors with appropriate insulation to prevent energy losses and protect against environmental conditions
Low Voltage Cables are typically designed for voltages less than 1000 volts and are used in buildings, offices, and factories
High Voltage Cables are used for transmitting power over long distances and in high voltage networks
2Telecommunication Cables
These cables are used to transmit audio and data signals in telecommunications networks. Telecommunication cables can be of the following types
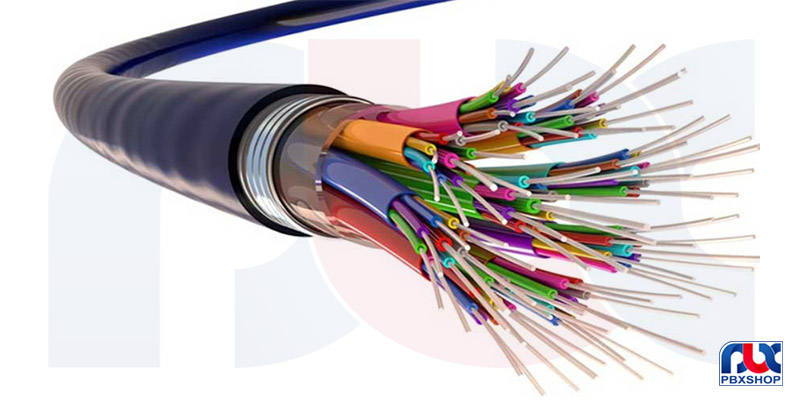
Twisted Pair Cables: Used for transmitting phone signals and data networks over short to medium distances
Fiber Optic Cables: Used for transmitting data at high speeds over long distances. These cables use glass or plastic strands to carry light signals
3Signal Transmission Cables
These cables are used to transmit analog or digital signals in audio, video, and automation systems. Signal transmission cables include coaxial cables and fiber optic cables, each with specific features
Coaxial Cables: Typically used for transmitting television, internet, and data signals. These cables have a central conductor, insulation, shielding layer, and outer sheath to protect signals from external interference
4Control Cables
Control cables are primarily used in industrial systems and automation for controlling and monitoring various processes. These cables consist of several strands of wire with copper or aluminum conductors, each separately insulated. They are commonly used for transmitting control signals and information in electrical and industrial automation systems
5Instrumentation Cables
These cables are used to transmit signals and data from instrumentation equipment and sensors to controllers and processing devices. Instrumentation cables are designed to be resistant to electromagnetic interference and challenging environmental conditions
6Network Cables
Network cables are used to connect computers and network devices to each other and transmit data in LAN and WAN systems. The most common types of these cables include
Ethernet Cables: For local area networks and high-speed data transmission
Fiber Optic Cables: For high-speed networks and long-distance data transmission
7Other Cables
In addition to the above types, other cables are designed for specific applications, such as
Thermal Cables: For resistance to high temperatures in specialized industries
Underwater Cables: For transmitting data or electricity underwater, such as in seas or lakes
Shielded and Armored Cables: For protection against electromagnetic interference and physical damage, especially in industrial and workshop environments
Applications of Different Wires and Cables
Depending on their structural features, cables have various applications. Some of the most important applications for different wires and cables include
Copper Cables: Used in power transmission lines, telecommunications, lighting systems, and electronic equipment
Aluminum Cables: Suitable for low voltage power transmission and distribution networks
Shielded Cables: Used in telecommunications and computer networks where noise and signal interference need to be minimized
Armored Cables: Used in industrial environments and construction projects where cables need to be protected against mechanical damage
Conclusion
Wires and cables are designed in various forms to suit specific applications. The selection of the right cable depends on the type of use, environmental conditions, and the technical specifications of the project. From copper and aluminum cables to fiber optics and instrumentation cables, each type has characteristics that make it suitable for specific uses
When selecting wires and cables, it’s essential to consider quality standards, reliability, and longevity to ensure optimal performance and safety for your system




